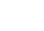Laser Doping
Contact: Francesca Chiodi
Laser Doping Principles
In the Pulsed Laser Induced Epitaxy, or PLIE technique, the transient surface melting of Silicon induced by a laser pulse of duration ~ 25 ns takes place over a thickness of 5 to 500 nm allowing a rapid mixing of the atoms of different nature in the molten zone. The ensuing rapid crystalisation - at a velocity of a few m/s – initiates at the boundary with the underlying crystal, and leads to a stable material. Preliminary modification of chemical surface bonds (through chimisorbtion) allows one to adjust the energy balance and the desorption or incorporation of surface ad atoms. The introduction of such new atomic species can be done before laser treatment through deposition or implantation, or during the treatment through the exposure of the surface to a gaseous atmosphere or chemisorbed layer. One then speaks of Gas Immersion Laser Doping or GILD. These processes allow one to obtain samples with chemical composition inaccessible by other means
Applications of laser treatment: GILD and PLIE
The very low energy input on the surface allows one to act without deteriorating the underlying material structure. This structure can be under strong strain, which allows applications in strain engineering for microelectronics and other microtechnologies.
Application to micro-nanoresonators (in collaboration with C2N – MiNaSys)
As a result of strain engineering, the resonance frequency of a Silicon nanobridge can be enhanced by up to a factor 40 after GILD. Artificially induced strains can amount up to 4 GPa.
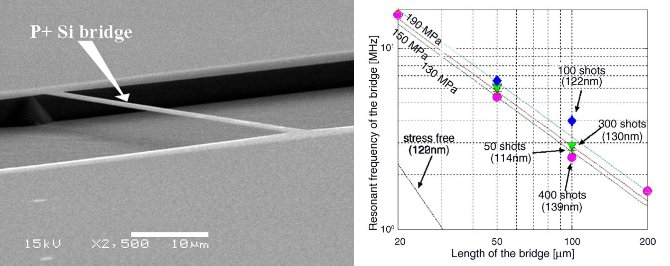
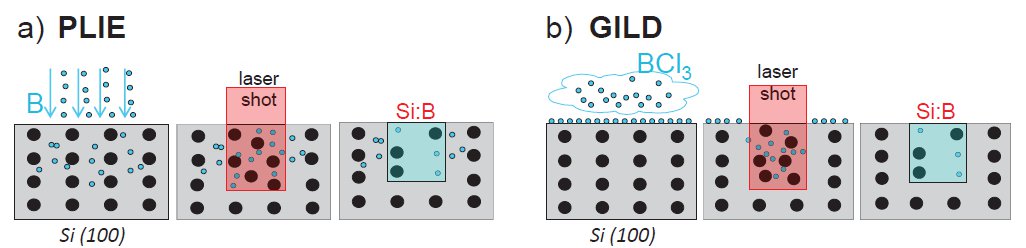
Example of a 120 nm wide nanobridge (left hand panel, SEM image) and resonance frequencies of the nanobridge for different doping levels, lengths, and thicknesses (right hand panel).
Application to the modification, by strain, of the structure of Germanium by phosphorus doping
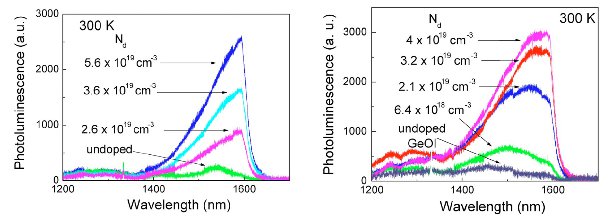
Ambient temperature luminescence spectra of bulk Germanium (left hand panel) and GeOI (right hand panel) after GILD Phosphorus doping. The detector is limited to the wavelength range below 1590 nm.
Publications
- J. L. Lábár, B. Pécz, A. van Waveren, G. Hallais, L. Desvignes, and F. Chiodi, Strain Measurement in Single Crystals by 4D-ED, Nanomaterials, 13(6), 1007 (2023)
- G. Hallais, G. Patriarche, L. Desvignes, D. Débarre and F. Chiodi, STEM analysis of deformation and B distribution in nanosecond laser ultra-doped Si1-x Bx, Semicond. Sci. Tech., 38, 034003 (2023)
- L. Vincent, F. Fossard, T. Kociniewski, L. Largeau, N. Cherkashin, M.J. H¨ytch, D. Débarre, T. Sauvage, A. Claverie, J. Boulmer, D. Bouchier, Nanoscale concentration and strain distribution in pseudomorphic films Si1−xGex/Si processed by pulsed laser induced epitaxy, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 9208– 9212 (2012)
- K. Hoummada, F. Dahlem, T. Kociniewski, J. Boulmer, C. Dubois, G. Prudon, E. Bustarret, H. Courtois, D. D�ebarre, and D. Mangelinck, Absence of boron aggregates in superconducting silicon confirmed by atom probe tomography, Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 182602 (2012)
- A. Bhaduri, T. Kociniewski, F. Fossard, J. Boulmer, D. Débarre, Optical and electrical properties of laser doped Si:B in the alloy range, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 9228 (2012)
- T. Kociniewski, F. Fossard, J.-L. Perrossier, D. Débarre, and J. Boulmer, Pseudomorphic and relaxed SiGe/Si(001) layer synthesis by gas immersion laser doping (GILD), Phys. Status Solidi C 8, 3, 915–918 (2011)
- F. Fossard, J. Boulmer, D. Débarre, J.L. Perrossier, C. Bachelet, F. Fortuna, V. Mathet, and D. Bouchier, Pseudomorphic SiGe/Si(001) layers synthesized by gas immersion laser doping, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 021911 (2008)
- D. Cammilleri, F. Fossard, D. Débarre, C. Tran Manh, C. Dubois, E. Bustarret, C. Marcenat, P. Achatz, D. Bouchier, J Boulmer, Highly doped Si and Ge formed by GILD (gas immersion laser doping) from GILD to superconducting silicon, Thin Solid Films 517, 75 (2008)
- D. Cammilleri, F. Fossard, M. Halbwax, C. Tran Manh, N. Yam, D. Débarre, J. Boulmer, D. Bouchier, Localized laser thermal annealing of nanometric SiGe layers protected by a dielectric Bragg mirror, Thin Solid Films 517, 327 (2008)
- T.Sarnet, G. Kerrien, N Yaakoubi., A. Bosseboeuf, E. Dufour-Gergam, D. Débarre, J. Boulmer, K. Kakushima, C. Laviron, M. Hernandez, J. Venturini, Laser doping for microelectronics and microtechnology, Appl. Surf. Science, 247, 1-4, 537 (2005)
- G. Kerrien, T. Sarnet, D. Débarre, J. Boulmer, M. Hernandez, C. Laviron, M.-N Séméria, Gas immersion laser doping (GILD) for ultra-shallow junction formation, Thin Solid Films, 453-454, 106 (2004)
- J. Venturini, M. Hernandez, G. Kerrien, C. Laviron, D. Camel, J. Santailler, T. Sarnet, J.Boulmer, Excimer laser thermal processing of ultra-shallow junctions: laser pulse duration, Thin Solid Films, 453-454, 145 (2004)
- G. Kerrien, J. Boulmer, D. Débarre, D. Bouchier, A. Grouillet, D. Lenoble, Ultra-shallow, super-doped and box-like junctions realized by laser-induced doping, Appl. Surf. Science, 186, 45 (2002)